
HAPPY LIFE

WHAT NEWS?

GitLab Issues Critical Security Patches for XSS and DoS Flaws

GitLab has rolled out emergency updates fixing 10 security flaws — including several high-severity XSS bugs and denial-of-service vulnerabilities — urging all self-managed customers to update without delay. The patches address critical risks across both Community and Enterprise editions that could allow attackers to execute malicious scripts, disrupt services, or bypass authentication.
itLab has released critical security updates addressing a series of vulnerabilities—some of them high severity—affecting both its Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE) platforms. The patches, published on December 10, 2025, include new versions 18.6.2, 18.5.4, and 18.4.6, all of which GitLab strongly recommends for immediate installation.
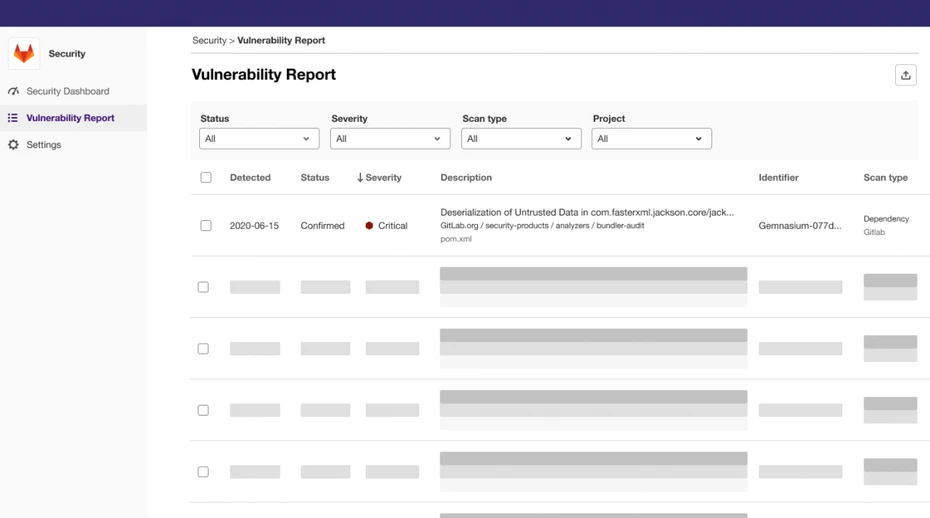
The latest security bulletin outlines a total of ten vulnerabilities, ranging from high-severity cross-site scripting flaws to denial-of-service weaknesses and information disclosure bugs. Four of the issues were classified as high severity and require urgent attention from administrators running self-managed instances.
CVSS 8.7 - XSS in Wiki functionality
CVSS 8.7 - Improper encoding / HTML injection in vulnerability reports
CVSS 8.0 - XSS in Swagger UI
CVSS 7.5 - GraphQL denial-of-service
GitLab says these vulnerabilities could allow attackers to run malicious scripts, manipulate content, or disrupt service availability. The GraphQL issue is especially concerning because it can be exploited by unauthenticated users, who may craft complex queries capable of overwhelming system resources and causing denial of service.
"These vulnerabilities pose serious risks to organizations using unpatched versions," explained security researcher Maria Chen. "The XSS flaws could allow attackers to steal session cookies, hijack accounts, or perform actions on behalf of authenticated users. The GraphQL DoS vulnerability is particularly dangerous as it doesn't require authentication and can bring down entire instances."
Among the patched vulnerabilities is CVE-2025-11984 (CVSS 6.8), an authentication bypass issue affecting WebAuthn two-factor authentication. While rated medium severity, this vulnerability could allow attackers to bypass 2FA protections under specific conditions, potentially granting unauthorized access to sensitive repositories and CI/CD pipelines.
Beyond the high-severity issues, GitLab's security release addresses several medium-severity vulnerabilities that could still pose risks to organizations:
Denial-of-service via crafted image metadata processing
Resource exhaustion through malformed commit requests
Multiple DoS vectors in GraphQL query processing
Error details exposure in API responses
Content manipulation in merge request titles
Improper input validation in multiple components
Administrators running versions 18.4.5 and earlier, 18.5.x before 18.5.4, or 18.6.x before 18.6.2 remain vulnerable to these exploits. GitLab.com users are already protected, as the hosted platform has been updated to the patched versions automatically. The company noted that the update includes database migrations, which may lead to downtime for single-node deployments.
GitLab strongly recommends that all self-managed customers apply the updates immediately. The company has provided clear upgrade paths and version recommendations based on current deployments:
Recommended Update
Update to 18.6.2 immediately
Update to 18.5.4 immediately
Update to 18.4.6 immediately
Upgrade to supported release first
Security analysts emphasize that organizations should treat these updates as a priority, especially given the potential for XSS-based account compromise and DoS-related service outages. Multi-node systems configured for zero-downtime upgrades can apply the patch without service interruption, while single-node deployments should schedule maintenance windows.
| CVE ID | CVSS | Severity | Impact | Affected Components |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2025-12716 | 8.7 | High | Cross-site Scripting (XSS) | Wiki functionality |
| CVE-2025-8405 | 8.7 | High | HTML Injection / Improper Encoding | Vulnerability reports |
| CVE-2025-12029 | 8.0 | High | Cross-site Scripting (XSS) | Swagger UI |
| CVE-2025-12562 | 7.5 | High | Denial of Service (DoS) | GraphQL API |
| CVE-2025-11984 | 6.8 | Medium | Authentication Bypass | WebAuthn 2FA |
| CVE-2025-12561 | 6.5 | Medium | Denial of Service (DoS) | ExifTool processing |
| CVE-2025-12563 | 6.5 | Medium | Denial of Service (DoS) | Commit API |
| CVE-2025-12564 | 5.3 | Medium | Information Disclosure | Error details exposure |
GitLab has provided detailed update guidance for different deployment scenarios. The update process varies depending on the installation method and current version:
Security researchers have analyzed the potential impact of these vulnerabilities in real-world scenarios:
XSS flaws allow client-side attacks against authenticated users
WebAuthn bypass could compromise 2FA-protected accounts
DoS vulnerabilities could disrupt development workflows
Information disclosure may reveal system details to attackers
Compromised GitLab instances could affect downstream deployments
Unpatched systems may violate security standards and regulations
GitLab Dedicated customers do not need to take action, as their instances receive managed updates directly from GitLab. However, all self-managed customers—including those using GitLab Community Edition—must apply these updates manually. The company has emphasized that there are no workarounds available for most of these vulnerabilities, making updates the only effective mitigation.
Organizations that cannot immediately apply updates should implement enhanced monitoring and consider temporary mitigations:
Further details, including impacted version ranges and patch notes, are available in GitLab's official security release documentation. Security teams are encouraged to review the complete advisories and coordinate with development teams to schedule updates during appropriate maintenance windows.